
No part of the active log can ever be truncated.
#ACID PROPERTIES SQL FULL#
This is the section of the log required to a full recovery of the database. The section of the log file from the first log record that must be present for a successful database-wide rollback to the last-written log record is called the active part of the log, active log, or tail of the log. This reserved space is freed when the transaction is completed. The amount of space reserved depends on the operations performed in the transaction, but generally it's equal to the amount of space used to log each operation. Each transaction reserves space in the transaction log to make sure that enough log space exists to support a rollback that is caused by either an explicit rollback statement, or if an error is encountered.
Modifications include changes by system stored procedures or data definition language (DDL) statements to any table, including system tables.Įvery extent and page allocation or deallocation. These operations include:Įvery data modification (insert, update, or delete). Many types of operations are recorded in the transaction log.

To roll forward the operation, the after image is applied.To roll back the logical operation, the reverse logical operation is performed.To roll forward the logical operation, the operation is performed again.The steps to recover an operation depend on the type of log record: The before image is a copy of the data before the operation is performed the after image is a copy of the data after the operation has been performed. Log records for data modifications record either the logical operation performed, or they record the before and after images of the modified data. For examples of LSNs, look at the output of sys.dm_db_log_info DMV and examine the vlf_create_lsn column. Here's an example of an LSN: 00000031:00000da0:0001, where 0x31 is the ID of the VLF, 0xda0 is the log block ID, and 0x1 is the first log record in that log block. For more information, see the VLF and log block sections. For each transaction, all log records associated with the transaction are individually linked in a chain using backward pointers that speed the rollback of the transaction. Each log record contains the ID of the transaction that it belongs to.
#ACID PROPERTIES SQL SERIAL#
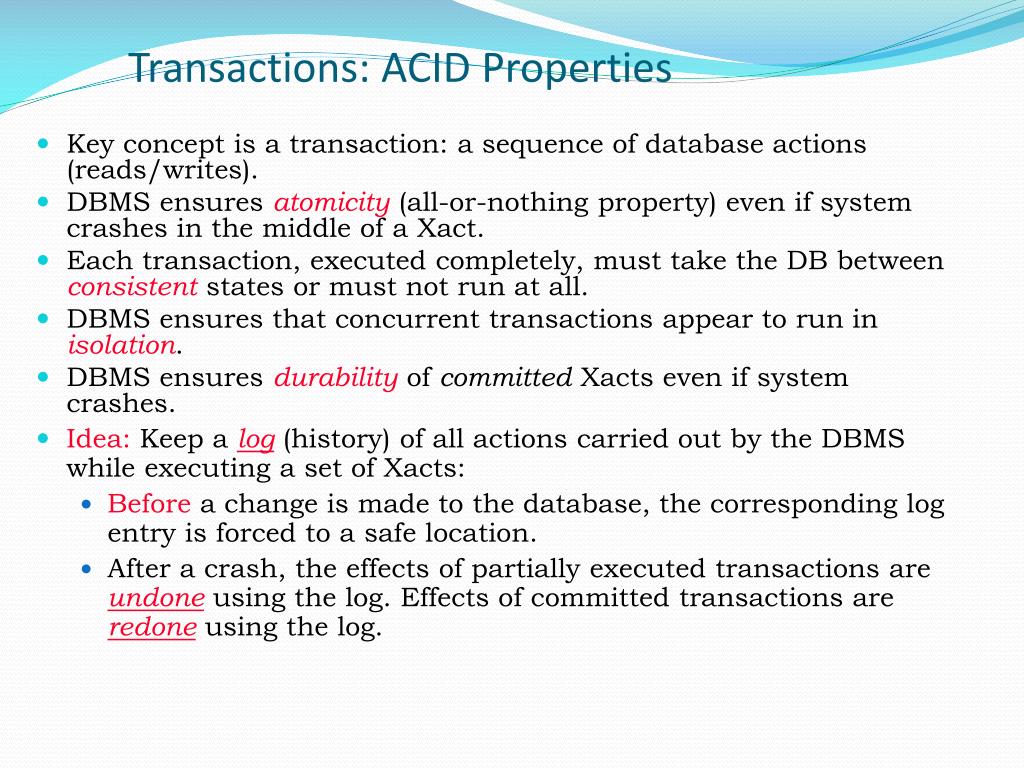
Log records are stored in a serial sequence as they're created, such that if LSN2 is greater than LSN1, the change described by the log record referred to by LSN2 occurred after the change described by the log record LSN1. Each new log record is written to the logical end of the log with an LSN that is higher than the LSN of the record before it.
Each log record is identified by a log sequence number (LSN). The SQL Server transaction log operates logically as if the transaction log is a string of log records. Understanding the architecture can improve your effectiveness in managing transaction logs. This guide provides information about the physical and logical architecture of the transaction log. The transaction log is a critical component of the database and, if there's a system failure, the transaction log might be required to bring your database back to a consistent state. Durability is often achieved through separate transaction logs that can "re-create" all transactions from some picked point in time (like a backup).Applies to: SQL Server Azure SQL Database Azure SQL Managed Instance Azure Synapse Analytics Analytics Platform System (PDW)Įvery SQL Server database has a transaction log that records all transactions and the database modifications that are made by each transaction. Only when the withdrawal transaction commits successfully and the teller looks at the balance again will the new balance be reported.ĭurability - A system crash or any other failure must not be allowed to lose the results of a transaction or the contents of the database.
Isolation - a teller looking up a balance must be isolated from a concurrent transaction involving a withdrawal from the same account. If the deposit operation failed, you don’t want the withdrawal operation to happen either.Ĭonsistency - a database tracking a checking account may only allow unique check numbers to exist for each transaction Atomicity - a transaction to transfer funds from one account to another involves making a withdrawal operation from the first account and a deposit operation on the second.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
